Metaphors are powerful tools in the English language, allowing us to understand abstract concepts by relating them to more concrete experiences. Storms, with their dramatic and often destructive nature, provide a rich source of metaphorical imagery. Understanding how storms are used metaphorically can significantly enhance your comprehension of literature, improve your writing, and deepen your appreciation for the nuances of the English language. This article will guide you through the various types of storm metaphors, their structural elements, usage rules, and common pitfalls, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate these linguistic tempests with confidence. Whether you’re a student, writer, or language enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will illuminate the power and beauty of storm metaphors.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition: Metaphors About Storms
- Classification of Storm Metaphors
- Function of Storm Metaphors
- Contexts for Using Storm Metaphors
- Structural Breakdown of Storm Metaphors
- Source Domain: Storms
- Target Domain: Abstract Concepts
- Linking Elements: Shared Characteristics
- Types and Categories of Storm Metaphors
- Emotional Turmoil
- Social Upheaval
- Personal Challenges
- Intellectual Struggles
- Relationship Difficulties
- Examples of Storm Metaphors
- Examples: Emotional Turmoil
- Examples: Social Upheaval
- Examples: Personal Challenges
- Examples: Intellectual Struggles
- Examples: Relationship Difficulties
- Usage Rules for Storm Metaphors
- Appropriateness and Context
- Consistency and Clarity
- Avoiding Overuse
- Common Mistakes with Storm Metaphors
- Mixed Metaphors
- Cliches and Overused Phrases
- Inappropriate Use of Intensity
- Practice Exercises
- Exercise 1: Identifying Storm Metaphors
- Exercise 2: Creating Storm Metaphors
- Exercise 3: Correcting Inappropriate Metaphors
- Advanced Topics in Storm Metaphors
- Extended Storm Metaphors
- Submerged Storm Metaphors
- Literary Analysis of Storm Metaphors
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Definition: Metaphors About Storms
A metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things, asserting that one thing *is* another to highlight a shared quality or characteristic. Metaphors about storms use the imagery of storms – including rain, wind, thunder, lightning, and associated destruction – to describe abstract concepts, emotions, situations, or experiences. These metaphors leverage the inherent drama and intensity of storms to add depth and impact to the description. The power of a storm metaphor lies in its ability to evoke vivid images and strong emotions in the reader or listener.
Classification of Storm Metaphors
Storm metaphors can be classified based on the specific aspect of the storm being emphasized. For example, a metaphor might focus on the destructive power of a hurricane, the cleansing effect of rain, or the suddenness of a lightning strike. Understanding these classifications allows for a more nuanced interpretation and application of storm metaphors. Consider how the specific elements of a storm – its intensity, duration, and aftermath – contribute to the overall metaphorical meaning.
Function of Storm Metaphors
The primary function of a storm metaphor is to create a more vivid and impactful description. By drawing a parallel between an abstract concept and the concrete image of a storm, the metaphor can help the audience better understand and connect with the idea being presented. Storm metaphors can also be used to evoke specific emotions, such as fear, anxiety, or even a sense of catharsis. The function goes beyond simple description; it aims to create a deeper emotional and intellectual resonance.
Contexts for Using Storm Metaphors
Storm metaphors are versatile and can be used in a variety of contexts, including literature, poetry, journalism, and everyday conversation. They are particularly effective when describing situations involving conflict, change, or intense emotions. However, it is important to consider the specific context and audience when using storm metaphors to ensure that they are appropriate and effective. A political speech might use storm metaphors to describe societal unrest, while a personal essay might use them to depict inner struggles.
Structural Breakdown of Storm Metaphors
Understanding the structure of a storm metaphor involves identifying the source domain (the storm) and the target domain (the abstract concept), and then recognizing the linking elements that connect the two. This breakdown helps to analyze how the metaphor functions and what specific qualities are being transferred.
Source Domain: Storms
The source domain in a storm metaphor is the storm itself. This includes all the elements associated with storms, such as rain, wind, thunder, lightning, clouds, and the resulting damage. The specific characteristics of the storm that are highlighted in the metaphor will influence the overall meaning. A gentle rain might represent a period of quiet reflection, while a violent hurricane could symbolize overwhelming chaos.
Target Domain: Abstract Concepts
The target domain is the abstract concept, emotion, or situation that the storm metaphor is used to describe. This could be anything from emotional turmoil to political unrest. The effectiveness of the metaphor depends on how well the characteristics of the storm align with the qualities of the target domain. For instance, if the target domain is “grief,” the metaphor might focus on the overwhelming and destructive nature of a storm.
Linking Elements: Shared Characteristics
The linking elements are the shared characteristics between the source domain (storm) and the target domain (abstract concept). These are the qualities that make the metaphor meaningful and effective. For example, the “intensity” of a storm might be linked to the “intensity” of an emotion. Identifying these linking elements is crucial for understanding the intended meaning of the metaphor. The shared characteristics provide the bridge between the literal image of the storm and the abstract idea being conveyed.
Types and Categories of Storm Metaphors
Storm metaphors can be categorized based on the specific type of abstract concept they are used to describe. Common categories include emotional turmoil, social upheaval, personal challenges, intellectual struggles, and relationship difficulties. Each category utilizes different aspects of storm imagery to convey the intended meaning.
Emotional Turmoil
Storm metaphors are frequently used to describe intense emotional states such as anger, grief, fear, and anxiety. The chaotic and overwhelming nature of a storm mirrors the internal chaos and distress experienced during emotional turmoil. Phrases like “a storm of emotions” or “a torrent of tears” are common examples.
Social Upheaval
Storm metaphors can effectively depict periods of social unrest, political instability, or widespread change. The destructive power of a storm can symbolize the disruption and chaos that accompany social upheaval. Examples include “a political storm brewing” or “the hurricane of revolution.”
Personal Challenges
Difficulties and obstacles in one’s personal life can be described using storm metaphors. This can include financial struggles, health problems, or career setbacks. The metaphor highlights the challenging and often overwhelming nature of these experiences. “Facing the storm of unemployment” or “battling the storm of illness” are illustrative examples.
Intellectual Struggles
The process of grappling with complex ideas or facing intellectual challenges can also be described using storm metaphors. The metaphor conveys the effort, confusion, and potential breakthroughs that can occur during intellectual pursuits. Phrases like “a brainstorm of ideas” or “navigating the storm of research” capture this concept.
Relationship Difficulties
Conflicts and challenges within relationships can be effectively portrayed using storm metaphors. The metaphor highlights the tension, turbulence, and potential for damage that can arise in strained relationships. Examples include “a stormy relationship” or “weathering the storm of a divorce.”
Examples of Storm Metaphors
This section provides a comprehensive collection of storm metaphors, organized by category, to illustrate their diverse applications and meanings. Each table includes numerous examples, showcasing the versatility of storm metaphors in conveying different abstract concepts.
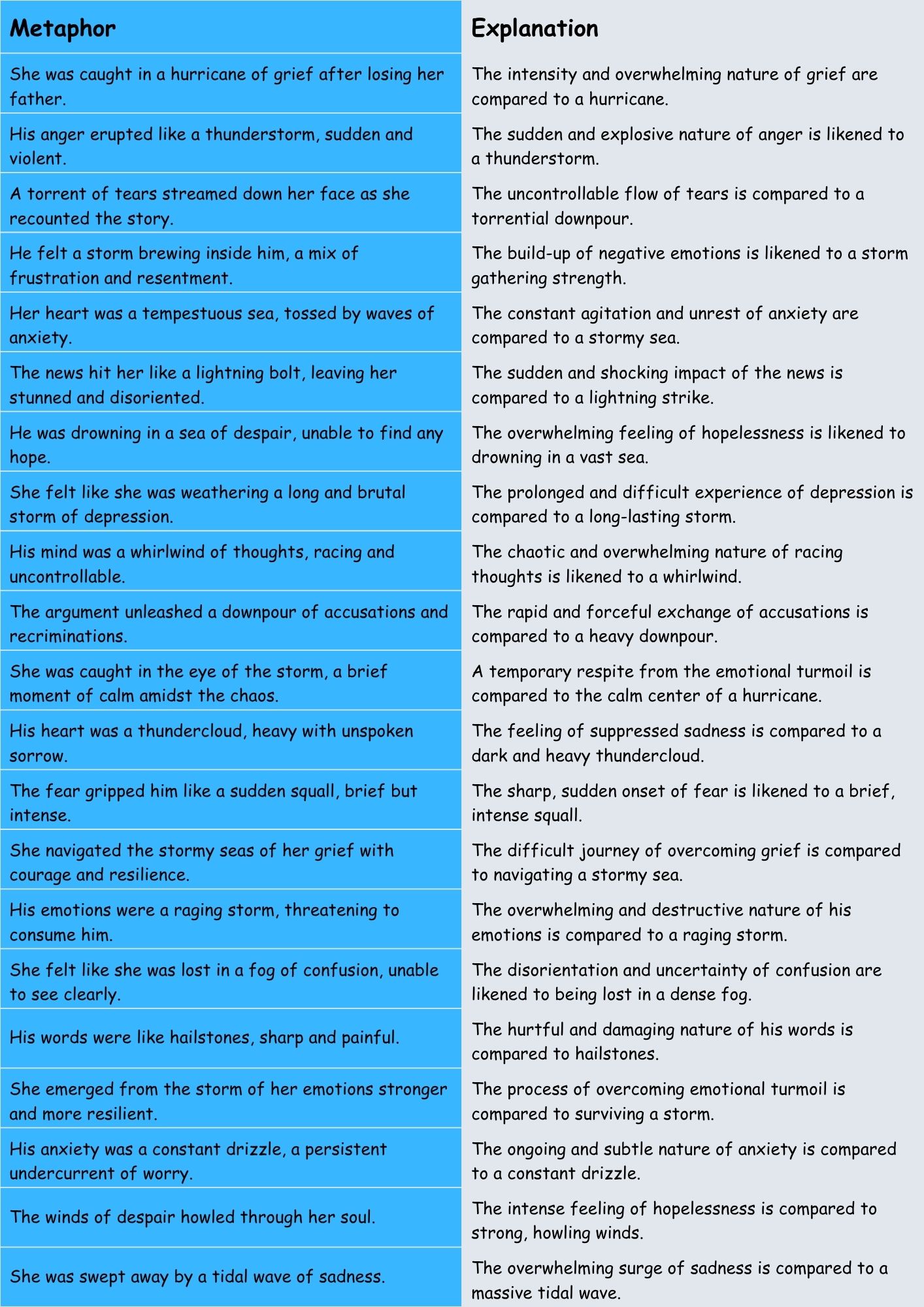
Examples: Emotional Turmoil
The following table provides examples of storm metaphors used to describe emotional turmoil. Notice how each example utilizes different aspects of storm imagery to convey the intensity and nature of the emotion.
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| She was caught in a hurricane of grief after losing her father. | The intensity and overwhelming nature of grief are compared to a hurricane. |
| His anger erupted like a thunderstorm, sudden and violent. | The sudden and explosive nature of anger is likened to a thunderstorm. |
| A torrent of tears streamed down her face as she recounted the story. | The uncontrollable flow of tears is compared to a torrential downpour. |
| He felt a storm brewing inside him, a mix of frustration and resentment. | The build-up of negative emotions is likened to a storm gathering strength. |
| Her heart was a tempestuous sea, tossed by waves of anxiety. | The constant agitation and unrest of anxiety are compared to a stormy sea. |
| The news hit her like a lightning bolt, leaving her stunned and disoriented. | The sudden and shocking impact of the news is compared to a lightning strike. |
| He was drowning in a sea of despair, unable to find any hope. | The overwhelming feeling of hopelessness is likened to drowning in a vast sea. |
| She felt like she was weathering a long and brutal storm of depression. | The prolonged and difficult experience of depression is compared to a long-lasting storm. |
| His mind was a whirlwind of thoughts, racing and uncontrollable. | The chaotic and overwhelming nature of racing thoughts is likened to a whirlwind. |
| The argument unleashed a downpour of accusations and recriminations. | The rapid and forceful exchange of accusations is compared to a heavy downpour. |
| She was caught in the eye of the storm, a brief moment of calm amidst the chaos. | A temporary respite from the emotional turmoil is compared to the calm center of a hurricane. |
| His heart was a thundercloud, heavy with unspoken sorrow. | The feeling of suppressed sadness is compared to a dark and heavy thundercloud. |
| The fear gripped him like a sudden squall, brief but intense. | The sharp, sudden onset of fear is likened to a brief, intense squall. |
| She navigated the stormy seas of her grief with courage and resilience. | The difficult journey of overcoming grief is compared to navigating a stormy sea. |
| His emotions were a raging storm, threatening to consume him. | The overwhelming and destructive nature of his emotions is compared to a raging storm. |
| She felt like she was lost in a fog of confusion, unable to see clearly. | The disorientation and uncertainty of confusion are likened to being lost in a dense fog. |
| His words were like hailstones, sharp and painful. | The hurtful and damaging nature of his words is compared to hailstones. |
| She emerged from the storm of her emotions stronger and more resilient. | The process of overcoming emotional turmoil is compared to surviving a storm. |
| His anxiety was a constant drizzle, a persistent undercurrent of worry. | The ongoing and subtle nature of anxiety is compared to a constant drizzle. |
| The winds of despair howled through her soul. | The intense feeling of hopelessness is compared to strong, howling winds. |
| She was swept away by a tidal wave of sadness. | The overwhelming surge of sadness is compared to a massive tidal wave. |
Examples: Social Upheaval
The following table illustrates how storm metaphors can be used to describe social upheaval. The focus is on the disruptive and transformative nature of these events.
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| A political storm is brewing in the nation’s capital. | The anticipation of political unrest and change is likened to a brewing storm. |
| The hurricane of revolution swept across the country, changing everything in its path. | The transformative and destructive power of a revolution is compared to a hurricane. |
| The protests unleashed a torrent of public anger. | The outpouring of public anger is compared to a torrential downpour. |
| The country is weathering a storm of economic crisis. | The challenging period of economic hardship is compared to enduring a storm. |
| The scandal created a whirlwind of controversy. | The rapid and chaotic spread of controversy is likened to a whirlwind. |
| The new policy was met with a hailstorm of criticism. | The intense and damaging criticism is compared to a hailstorm. |
| The nation is navigating the stormy seas of political division. | The difficult and challenging process of dealing with political division is compared to navigating a stormy sea. |
| The movement gained momentum like a gathering storm. | The increasing strength and potential impact of the movement are likened to a storm gathering strength. |
| The government is trying to calm the storm of public discontent. | The effort to address and alleviate public dissatisfaction is compared to calming a storm. |
| The changes swept through the industry like a tidal wave. | The massive and transformative impact of the changes is compared to a tidal wave. |
| The strike unleashed a tempest of labor unrest. | The intense and agitated state of labor relations is compared to a tempest. |
| The reforms were met with a thunderous opposition. | The strong and forceful resistance to the reforms is compared to thunder. |
| The city was plunged into a fog of uncertainty after the disaster. | The confusion and lack of clarity following the disaster are likened to being lost in a fog. |
| The investigation sparked a lightning rod of controversy. | The event that attracts intense and sudden controversy is compared to a lightning rod. |
| The riots were a raging storm of violence. | The uncontrolled and destructive nature of the riots is compared to a raging storm. |
| The community is still recovering from the aftermath of the storm. | The long-term consequences and challenges following a period of upheaval are compared to the aftermath of a storm. |
| The debate raged like a fierce squall. | The intense and sudden nature of the debate is compared to a fierce squall. |
| The company faced a blizzard of lawsuits. | The overwhelming number and intensity of lawsuits are compared to a blizzard. |
| The protests were a downpour of grievances. | The expression of numerous complaints and grievances is compared to a downpour. |
| The winds of change are blowing through the country. | The forces driving societal transformation are compared to strong winds. |
| The country is bracing for the storm of economic recession. | The anticipation of a challenging economic period is compared to preparing for a storm. |
Examples: Personal Challenges
This table provides examples of storm metaphors used to describe personal challenges. The examples focus on the difficulties and struggles individuals face in their lives.
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He is weathering a personal storm after losing his job. | The difficult period following job loss is compared to enduring a storm. |
| She is battling the storm of illness with incredible strength. | The struggle against illness is compared to fighting a storm. |
| He felt like he was drowning in a sea of debt. | The overwhelming burden of debt is likened to drowning in a vast sea. |
| She is navigating the stormy waters of adolescence. | The challenging period of adolescence is compared to navigating a stormy sea. |
| He is trying to stay afloat in the economic storm. | The struggle to maintain financial stability during economic hardship is compared to staying afloat in a storm. |
| She felt like she was lost in a fog of uncertainty about her future. | The confusion and lack of clarity about the future are likened to being lost in a fog. |
| He faced a hailstorm of criticism after his mistake. | The intense and damaging criticism he received is compared to a hailstorm. |
| She is emerging from the storm of addiction stronger and more resilient. | The process of overcoming addiction is compared to surviving a storm. |
| He is caught in a whirlwind of responsibilities. | The overwhelming and chaotic nature of numerous responsibilities is likened to a whirlwind. |
| She is trying to weather the storm of grief after her loss. | The difficult process of grieving is compared to enduring a storm. |
| He felt like he was hit by a lightning bolt of bad news. | The sudden and shocking impact of the bad news is compared to a lightning strike. |
| She is trying to calm the storm of anxiety that overwhelms her. | The effort to manage and alleviate anxiety is compared to calming a storm. |
| He found himself in the eye of the storm, a brief moment of peace amidst the chaos. | A temporary respite from the challenges is compared to the calm center of a hurricane. |
| She is bracing herself for the storm of change ahead. | The preparation for a period of significant change is compared to bracing for a storm. |
| He felt like he was swept away by a tidal wave of emotions. | The overwhelming surge of emotions is compared to a massive tidal wave. |
| She is navigating the tempestuous seas of her career. | The challenging and unpredictable nature of her career is compared to navigating a tempestuous sea. |
| He is trying to find solid ground after the storm of his divorce. | The effort to rebuild his life after a divorce is compared to finding solid ground after a storm. |
| She is facing a blizzard of challenges in her new role. | The overwhelming number and intensity of challenges are compared to a blizzard. |
| He felt like he was trapped in a never-ending storm of misfortune. | The feeling of continuous bad luck is compared to being trapped in a never-ending storm. |
| She is trying to shield her children from the storm of her financial problems. | The attempt to protect her children from the impact of financial difficulties is compared to shielding them from a storm. |
| He felt like the winds of fate were conspiring against him. | The feeling that external forces are working against him is compared to strong, conspiring winds. |
Examples: Intellectual Struggles
The following table demonstrates how storm metaphors can be applied to describe intellectual struggles and challenges.
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He had a brainstorm of ideas while working on the project. | A sudden and intense burst of creative ideas is compared to a brainstorm. |
| She is navigating the stormy waters of research for her dissertation. | The challenging and complex process of research is compared to navigating a stormy sea. |
| He felt lost in a fog of confusion while studying the complex theory. | The disorientation and lack of understanding are likened to being lost in a fog. |
| She is facing a hailstorm of questions during the debate. | The rapid and intense barrage of questions is compared to a hailstorm. |
| He is trying to weather the storm of criticism from his peers. | The effort to withstand criticism from colleagues is compared to enduring a storm. |
| The discussion unleashed a torrent of arguments. | The rapid and forceful exchange of arguments is compared to a torrential downpour. |
| He felt like he was drowning in a sea of information. | The overwhelming amount of information is likened to drowning in a vast sea. |
| She is trying to calm the storm of doubts that plague her mind. | The effort to manage and alleviate self-doubt is compared to calming a storm. |
| He found himself in the eye of the storm, a moment of clarity amidst the confusion. | A temporary moment of understanding is compared to the calm center of a hurricane. |
| She is bracing herself for the storm of the exam. | The preparation for a challenging exam is compared to bracing for a storm. |
| He felt like he was hit by a lightning bolt of inspiration. | The sudden and brilliant idea is compared to a lightning strike. |
| She is trying to navigate the tempestuous seas of philosophical debate. | The challenging and unpredictable nature of philosophical debate is compared to navigating a tempestuous sea. |
| He is trying to find solid ground after the storm of intellectual challenge. | The effort to consolidate understanding after a difficult intellectual challenge is compared to finding solid ground after a storm. |
| She is facing a blizzard of data in her research. | The overwhelming amount and complexity of data are compared to a blizzard. |
| His mind was a whirlwind of theories, constantly spinning and evolving. | The rapid and chaotic processing of multiple theories is likened to a whirlwind. |
| The lecture sparked a thunderstorm of questions from the students. | The sudden and intense outpouring of questions from the students is compared to a thunderstorm. |
| She felt like the winds of doubt were undermining her confidence. | The feeling that uncertainty is eroding her self-assurance is compared to undermining winds. |
| He is still recovering from the aftermath of the intellectual storm. | The process of assimilating and integrating new knowledge after a challenging intellectual experience is compared to recovering from the aftermath of a storm. |
| The project was a downpour of problems, each one more challenging than the last. | The continuous stream of problems encountered during the project is compared to a downpour. |
| He is trying to clear the fog of misunderstanding that surrounds the issue. | The effort to resolve confusion and clarify a complex issue is compared to clearing a fog. |
| She felt like she was caught in a cyclone of academic pressure. | The intense and overwhelming pressure of academic demands is compared to being caught in a cyclone. |
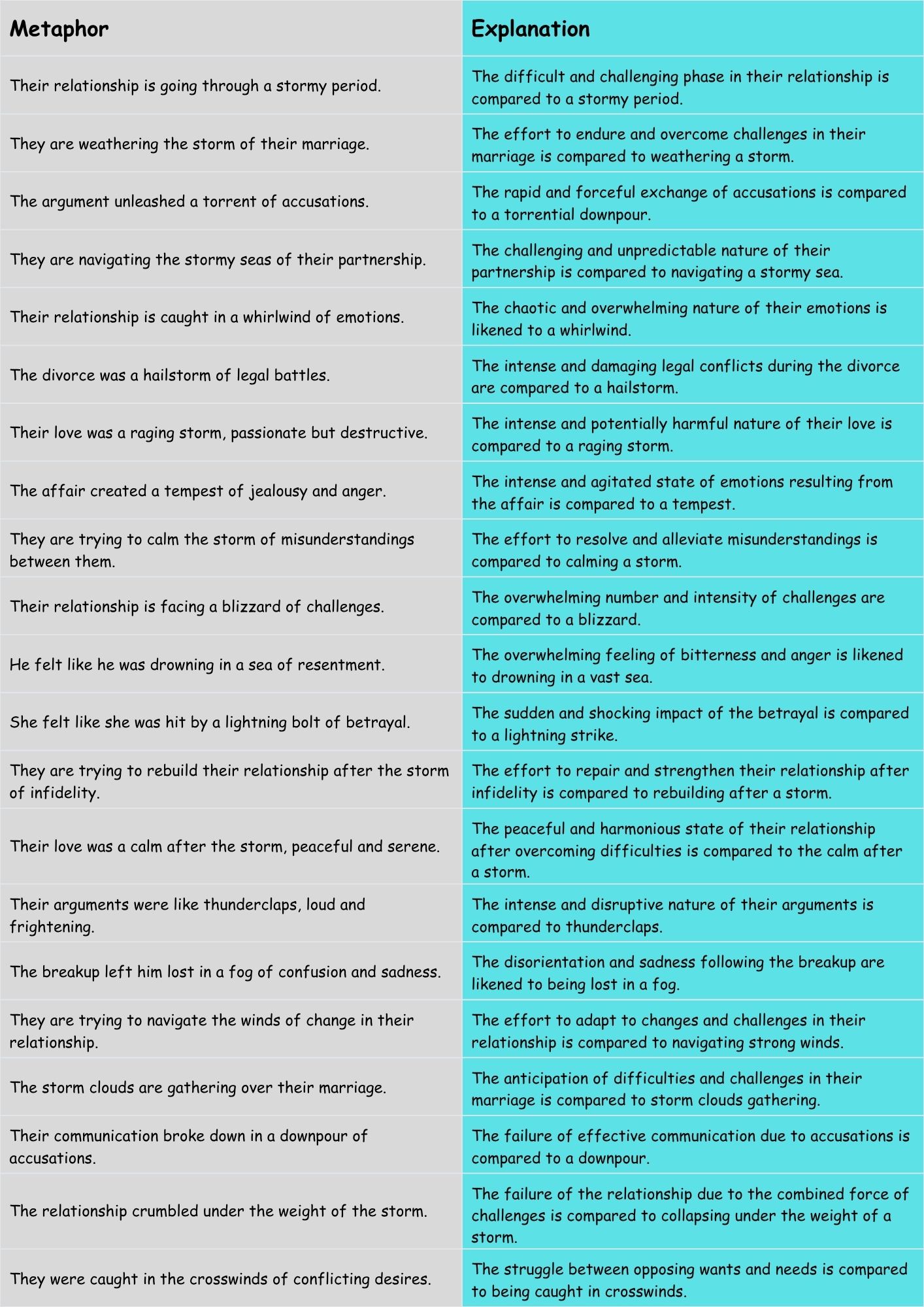
Examples: Relationship Difficulties
This table shows examples of storm metaphors used to describe the challenges and conflicts that can arise in relationships.
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Their relationship is going through a stormy period. | The difficult and challenging phase in their relationship is compared to a stormy period. |
| They are weathering the storm of their marriage. | The effort to endure and overcome challenges in their marriage is compared to weathering a storm. |
| The argument unleashed a torrent of accusations. | The rapid and forceful exchange of accusations is compared to a torrential downpour. |
| They are navigating the stormy seas of their partnership. | The challenging and unpredictable nature of their partnership is compared to navigating a stormy sea. |
| Their relationship is caught in a whirlwind of emotions. | The chaotic and overwhelming nature of their emotions is likened to a whirlwind. |
| The divorce was a hailstorm of legal battles. | The intense and damaging legal conflicts during the divorce are compared to a hailstorm. |
| Their love was a raging storm, passionate but destructive. | The intense and potentially harmful nature of their love is compared to a raging storm. |
| The affair created a tempest of jealousy and anger. | The intense and agitated state of emotions resulting from the affair is compared to a tempest. |
| They are trying to calm the storm of misunderstandings between them. | The effort to resolve and alleviate misunderstandings is compared to calming a storm. |
| Their relationship is facing a blizzard of challenges. | The overwhelming number and intensity of challenges are compared to a blizzard. |
| He felt like he was drowning in a sea of resentment. | The overwhelming feeling of bitterness and anger is likened to drowning in a vast sea. |
| She felt like she was hit by a lightning bolt of betrayal. | The sudden and shocking impact of the betrayal is compared to a lightning strike. |
| They are trying to rebuild their relationship after the storm of infidelity. | The effort to repair and strengthen their relationship after infidelity is compared to rebuilding after a storm. |
| Their love was a calm after the storm, peaceful and serene. | The peaceful and harmonious state of their relationship after overcoming difficulties is compared to the calm after a storm. |
| Their arguments were like thunderclaps, loud and frightening. | The intense and disruptive nature of their arguments is compared to thunderclaps. |
| The breakup left him lost in a fog of confusion and sadness. | The disorientation and sadness following the breakup are likened to being lost in a fog. |
| They are trying to navigate the winds of change in their relationship. | The effort to adapt to changes and challenges in their relationship is compared to navigating strong winds. |
| The storm clouds are gathering over their marriage. | The anticipation of difficulties and challenges in their marriage is compared to storm clouds gathering. |
| Their communication broke down in a downpour of accusations. | The failure of effective communication due to accusations is compared to a downpour. |
| The relationship crumbled under the weight of the storm. | The failure of the relationship due to the combined force of challenges is compared to collapsing under the weight of a storm. |
| They were caught in the crosswinds of conflicting desires. | The struggle between opposing wants and needs is compared to being caught in crosswinds. |
Usage Rules for Storm Metaphors
Using storm metaphors effectively requires careful consideration of several factors. It’s crucial to ensure that the metaphor is appropriate for the context, consistent with the overall tone, and not overused.
Appropriateness and Context
The appropriateness of a storm metaphor depends on the specific context and audience. A metaphor that is effective in a dramatic poem might be inappropriate in a formal business report. Consider the tone and purpose of your writing and choose metaphors that align with these elements.
Consistency and Clarity
Maintain consistency in your use of storm metaphors. Avoid mixing different types of storm imagery in a way that creates confusion or weakens the impact of the metaphor. Ensure that the connection between the storm imagery and the abstract concept is clear and easily understood.
Avoiding Overuse
Overusing storm metaphors can diminish their impact and make your writing sound cliché. Use them sparingly and strategically to maximize their effectiveness. Consider alternative metaphors or figures of speech to add variety to your writing.
Common Mistakes with Storm Metaphors
Several common mistakes can undermine the effectiveness of storm metaphors. These include using mixed metaphors, relying on cliches, and inappropriately using intensity.
Mixed Metaphors
A mixed metaphor combines two or more incompatible metaphors, creating a nonsensical or confusing image. For example, “He was drowning in a sea of debt, but he kept his head above water by climbing the ladder of success” mixes the “drowning in debt” metaphor with the “climbing the ladder of success” metaphor, creating a confusing and illogical image. Avoid mixing metaphors to maintain clarity and coherence.
Correct: He was drowning in a sea of debt.
Incorrect: He was drowning in a sea of debt, but he kept his head above water by climbing the ladder of success.
Cliches and Overused Phrases
Cliches are overused phrases that have lost their original impact. Using clichéd storm metaphors, such as “weathering the storm,” can make your writing sound unoriginal and uninspired. Strive to create fresh and original metaphors that capture the essence of the idea in a unique way.
Correct: The company faced a period of intense financial hardship.
Incorrect: The company was weathering the storm.
Inappropriate Use of Intensity
Using excessively intense storm metaphors to describe minor or insignificant situations can create a sense of exaggeration or hyperbole. Ensure that the intensity of the metaphor aligns with the significance of the situation being described. Choose metaphors that accurately reflect the scale and impact of the event or emotion.
Correct: She felt a mild sense of disappointment.
Incorrect: She was devastated by a hurricane of disappointment.
Practice Exercises
These exercises will help you practice identifying, creating, and correcting storm metaphors. Each exercise includes a series of questions with answers provided at the end.
Exercise 1: Identifying Storm Metaphors
Identify the storm metaphors in the following sentences and explain what they mean.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The company weathered the storm of the recession. | “Weathered the storm” is the metaphor. It means the company successfully survived the difficult period of the recession. |
| 2. His anger erupted like a thunderstorm. | “Erupted like a thunderstorm” is the metaphor. It means his anger was sudden, intense, and explosive. |
| 3. She was lost in a fog of confusion after the accident. | “Fog of confusion” is the metaphor. It means she felt disoriented and unclear about what happened after the accident. |
| 4. The debate unleashed a torrent of accusations. | “Torrent of accusations” is the metaphor. It means the debate involved a rapid and forceful exchange of accusations. |
| 5. The scandal created a whirlwind of controversy. | “Whirlwind of controversy” is the metaphor. It means the scandal caused a rapid and chaotic spread of public debate and disagreement. |
Exercise 2: Creating Storm Metaphors
Create storm metaphors for the following situations.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. Describe the feeling of being overwhelmed by work. | The workload was a tidal wave threatening to engulf me. |
| 2. Describe a sudden burst of creative inspiration. | Inspiration struck like a bolt of lightning, illuminating my mind. |
| 3. Describe a period of intense social change. | The country was undergoing a hurricane of transformation. |
| 4. Describe the feeling of constant anxiety. | Anxiety was a relentless drizzle, always present in the background. |
| 5. Describe a heated argument between two people. | Their argument turned into a fierce thunderstorm, filled with shouting and accusations. |
Exercise 3: Correcting Inappropriate Metaphors
Correct the following sentences to use more appropriate and effective storm metaphors.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He was as happy as a hurricane after winning the lottery. | He was as happy as a hurricane after winning the lottery. He was struck by a wave of elation after winning the lottery. |
| 2. The project was a light drizzle of challenges. | The project was a light drizzle of challenges. The project was a tempest of challenges. |
| 3. She weathered the light breeze of criticism. | She weathered the light breeze of criticism. She weathered the storm of criticism. |
| 4. His speech was a sunny day of ideas. | His speech was a sunny day of ideas. His speech was a brainstorm of ideas. |
| 5. The company was sailing smoothly through the storm of bankruptcy. | The company was sailing smoothly through the storm of bankruptcy. The company was struggling to stay afloat in the storm of bankruptcy. |
Advanced Topics in Storm Metaphors
Beyond the basic understanding of storm metaphors, there are more advanced applications and interpretations that can further enhance your understanding and use of this powerful literary device.
Extended Storm Metaphors
An extended metaphor is a metaphor that is developed over several lines or even throughout an entire work. In the context of storm metaphors, this could involve creating a complex and detailed comparison between a storm and an abstract concept, exploring various aspects of the storm and their corresponding elements in the target domain. Extended metaphors allow for a deeper and more nuanced exploration of the relationship between the source and target domains.
Submerged Storm Metaphors
A submerged metaphor, also known as an implicit metaphor, is a metaphor that is not explicitly stated but implied through the language used. In storm metaphors, this could involve using storm-related vocabulary and imagery without directly stating the comparison. Submerged metaphors can add subtlety and depth to writing, allowing the reader to draw their own connections and interpretations.
Literary Analysis of Storm Metaphors
Analyzing storm metaphors in literature involves examining how authors use storm imagery to convey deeper meanings and themes. This can include identifying the specific elements of the storm being emphasized, understanding the intended emotional impact, and exploring the cultural or historical context of the metaphor. Literary analysis of storm metaphors can provide valuable insights into the author’s intentions and the overall message of the work.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions about storm metaphors.
What’s the difference between a simile and a storm metaphor?
A simile uses “like” or “as” to make a comparison, while a metaphor directly equates two things. For example, “His anger was *like* a thunderstorm” is a simile, whereas “His anger *was* a thunderstorm” is a metaphor.
How do I avoid using clichéd storm metaphors?
Focus on creating original and specific comparisons. Instead of saying “weathering the storm,” describe the specific challenges and how they are being overcome using unique storm imagery.
Can storm metaphors be used in a positive way?
Yes, storm metaphors can be used to describe positive or transformative experiences. For example, a “brainstorm” of ideas or the “calm after the storm” can evoke positive imagery.
How can I improve my understanding of storm metaphors in literature?
Pay close attention to the specific details of the storm imagery used by the author and consider how these details relate to the overall themes and message of the work.
Are storm metaphors culturally universal?
While storms are a common phenomenon across cultures, the specific associations and meanings attached to them can vary. Consider the cultural context when interpreting storm metaphors.
Conclusion
Storm metaphors are a powerful and versatile tool for enriching your language and deepening your understanding of abstract concepts. By mastering the structural elements, usage rules, and common pitfalls of storm metaphors, you can effectively harness their expressive potential to create vivid and impactful writing. Whether you’re analyzing literature, crafting compelling narratives, or simply seeking to enhance your communication skills, a solid grasp of storm metaphors will undoubtedly prove invaluable. So, embrace the tempest, and let the power of storm metaphors illuminate your words.